
Teaching is an attractive profession for a range of reasons; as well as it being interesting, no two days being the same and it provides the chance to shape young people’s lives. Teacher’s pensions are also among the best and safest available.
Here’s what you need to know.
What are the current arrangements for teacher’s pensions?
The Teachers’ Pension Scheme is a ‘defined benefits’ pension scheme. That means it offers teachers a guaranteed income in retirement as opposed to a ‘defined contribution’ scheme, where income is based on the performance of the pension fund.
Teachers in England and Wales pay into the scheme direct from their salary each month and it is then topped up by their employer. Teachers based in Scotland have separate pension agreements.
In return for the money, they put in, teachers receive an index-linked (this means it increases in line with the cost of living) government-backed annual pension for retirement. This is based on their career average earnings.
Is this the case for all teachers?
In 2015, the government introduced reforms to public service pension schemes, including the Teachers’ Pension Scheme, which meant some members receiving Transitional Protection, remained in the final salary scheme, while others entered the career average scheme.
These changes have since been deemed discriminatory on age grounds and the legislation to correct this is being rolled out in two stages.
Part one of the legislation was the closure of the final salary scheme from 1 April 2022, with all active members now building up their pension in the career average scheme.
Part two will give eligible members the option to choose between their final salary and career average pension scheme benefits between 1 April 2015 and 31 March 22 (the remedy period).
How is the career average pension worked out?
A member will gain a part of their pension for every year they contribute to the Teachers’ Pension Scheme. This means that a teacher will add 1/57th to their ‘pot’, depending on the amount of their earnings and each year that’s increased in line with indexation. An example of how a career average pension can grow over five years can be seen below:
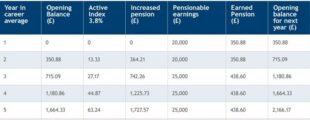
How much do teachers and employers contribute?
A teacher’s employer will deduct pension contributions from their pay before deducting tax, thereby giving tax relief on the pension contribution. Employers contribute the equivalent of 23.68% of a teacher’s pay towards the cost.
Contribution rates are determined by a teacher’s salary.
| Annual Salary Rate for the Eligible Employment from 1 April 2022 | Member Contribution Rate |
| Up to £29,187.99 | 7.4% |
| £29,188 to £39,290.99 | 8.6% |
| £39,291 to £46,586.99 | 9.6% |
| £46,587 to £61,742.99 | 10.2% |
| £61,743 to £84,193.99 | 11.3% |
| £84,194 and above | 11.7% |